TLDR: AI is transforming how businesses operate by automating tasks, improving decision-making, and unlocking new creative possibilities. By understanding how AI works, using the right tools, writing better prompts, and setting clear policies, businesses can start integrating AI into everyday workflows for greater efficiency and growth.
At a Glance:
- AI is broader than most people think. Artificial intelligence includes machine learning, deep learning, large language models, and generative AI. Each are designed to analyze data, recognize patterns, and create useful outputs.
- Businesses are already using AI to work smarter. From marketing content and predictive analytics to supply chain optimization, AI helps companies move faster and make better data-driven decisions.
- Better prompts lead to better results. Prompt engineering (using clear persona, context, task, examples, format, and tone) can dramatically improve the quality and usefulness of AI-generated responses.
- Responsible AI use starts with clear policies. Establishing an AI ethics policy and protecting sensitive information ensures teams can use AI productively while maintaining security, privacy, and accountability.
AI has completely transformed the way I work and the way my business runs. It has streamlined processes, sparked new ideas, and helped us move faster without losing focus on what matters most: people. Now, I want to help others experience the same kind of shift.
In this post, I am going to arm you with smart, actionable strategies to integrate AI into your operations. We’ll demystify AI—what it is (and what it’s not), explore real tools and applications, show how businesses are putting AI to work, and walk through practical tips you can start using today.
What is AI?
AI is everywhere—in schools, homes, and workplaces—and it’s talked about so often that many of us feel like we’ve got a solid handle on it. But AI wears many hats, and every once in a while, it’s worth revisiting the fundamentals.
Artificial intelligence is the broad concept of machines performing tasks that typically require human intelligence—things like recognizing patterns, making decisions, solving problems, and even understanding language. At its core, AI is about building systems that can learn, reason, and adapt.

Machine learning is a subset of AI. It focuses on training algorithms to learn from data and improve over time without being explicitly programmed. Think of it as teaching a computer to recognize patterns—like identifying spam emails or predicting customer behavior—by feeding it lots of examples.
Deep learning is a more advanced type of machine learning. It uses artificial neural networks (modeled after the human brain) with multiple layers to analyze complex data. This is the technology behind image recognition, natural language processing, and voice assistants like Siri or Alexa.
Discriminative models are all about drawing boundaries between categories. For example, if you want a model to tell whether an email is spam or not, a discriminative model learns the differences between the two and makes predictions accordingly. It’s focused on classification and decision-making based on known data.
Large Language Models (LLMs) like ChatGPT, Bard, or Claude are a type of deep learning model trained on massive amounts of text. They can understand, summarize, and generate human-like language. These models don’t just regurgitate data—they predict what comes next in a sentence based on patterns they’ve seen in their training.
Generative AI takes things a step further. It creates something new—text, images, code, music, even video—based on the data it has learned. Tools like ChatGPT, Midjourney, and DALL·E are examples. They don’t just process input; they generate fresh, useful output. That’s what makes them so powerful (and exciting!) for businesses and creatives.
Here are some tools you can turn to for a variety of applications:
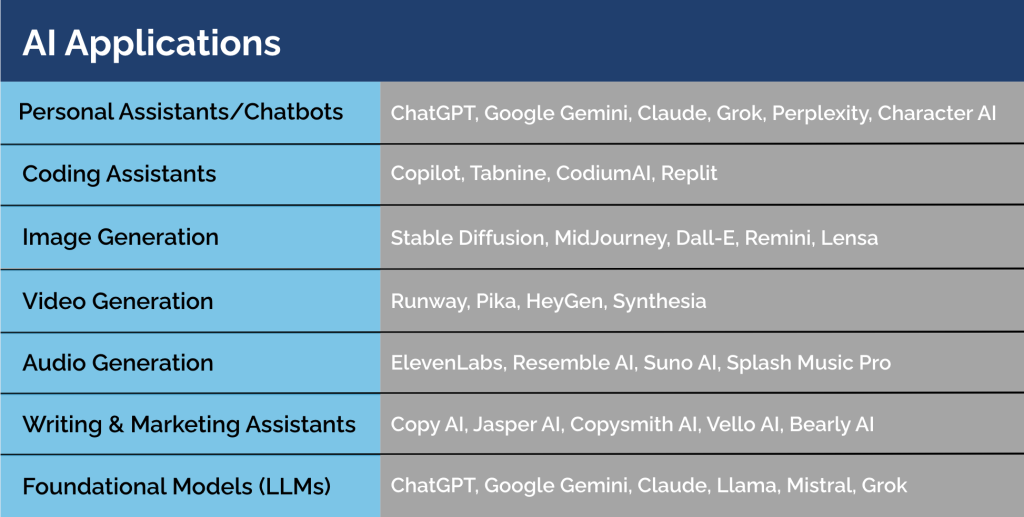
How are Businesses Using AI?
AI is helping businesses move faster, work smarter, and do more with less—and there’s no reason you shouldn’t be using it too.
In marketing and content creation, AI-powered tools can generate blog posts, ad copy, product descriptions, and social media content at scale. In supply chain management, AI can forecast demand, optimize inventory, and automate logistics planning.
One of the most impactful uses of AI is predictive analytics. By analyzing patterns in customer behavior, AI can forecast future actions—like who’s likely to make a purchase, cancel a subscription, or respond to a specific offer.
Here are a few examples of predictive analytics in action:
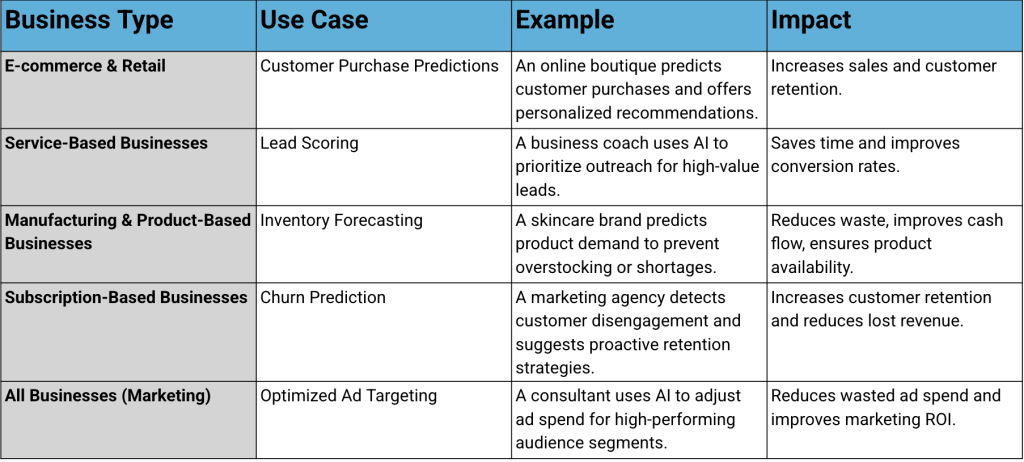
No matter the industry, there is a serious competitive advantage in using AI.
Let’s Talk About Prompting
Large Language Models (LLMs) are trained on massive amounts of internet data—and let’s face it, a lot of that data is just…average. If you give a bland prompt, you’ll likely get a bland response. These tools won’t default to brilliance—you have to lead them there.
That’s where prompt engineering comes in. It’s the art of asking the right questions in the right way to get the results you actually want. The better your prompt, the better the output.
Here’s a formula to help you get smart, specific, and genuinely helpful responses from AI every time:
- Persona: Tell the chatbot who you want them to be.
- Context – Explain the reason for the request.
- Task – Be specific and make the request for desired information.
- Example – Provide an example to help guide.
- Format – Request the format you want the answer in.
- Tone – Determine the tone you want the answer in.
AI is an incredibly powerful tool, and yes, you should absolutely be using it in the workplace. But before diving in, take a crucial first step: establish a clear AI Ethics Policy and make sure every employee understands and agrees to follow it.
A solid policy promotes transparency, helps mitigate bias, protects user privacy, and keeps your company accountable for AI-powered decisions.
To keep your business and your data safe, never share the following information in an AI prompt:
- Passwords
- Passports
- Credit Card Numbers
- Addresses
- Telephone Numbers
- Names
- Anything Confidential (i.e. Contracts)
- Personal Information
Take a Step Toward Smarter Work
Advancements in artificial intelligence are moving rapidly. Now is the perfect time to start integrating AI tools into your workflow to boost speed, efficiency, and impact.
Start by identifying areas of opportunity in your business. Where are you wasting time? Where do you need smarter decision-making? What repetitive tasks could AI take off your plate?
If you’re ready to explore the possibilities but not sure where to begin, lean on a trusted partner. Proof Digital has been tracking and testing AI from the start.
Let’s talk about how AI can drive real growth in your business. Contact us today.
FAQs
What is artificial intelligence (AI) in simple terms?
Artificial intelligence refers to technology that allows machines to perform tasks that typically require human intelligence. This includes analyzing data, recognizing patterns, solving problems, making predictions, and understanding language.
What is the difference between AI, machine learning, and generative AI?
AI is the broad concept of machines performing intelligent tasks. Machine learning is a subset of AI that allows systems to learn from data and improve over time. Generative AI is a type of AI that can create new content (such as text, images, or code) based on patterns it has learned.
How are businesses using AI today?
Businesses are using AI to automate repetitive tasks, generate marketing content, analyze customer data, forecast demand, improve customer service, and make better business decisions through predictive analytics.
What are large language models (LLMs)?
Large language models are advanced AI systems trained on massive datasets of text. They can understand prompts and generate human-like responses, summaries, and content. Popular examples include ChatGPT and Claude.
What is prompt engineering?
Prompt engineering is the process of writing clear and specific instructions for AI tools to generate better results. Including details like context, examples, tone, and formatting helps AI produce more accurate and useful responses.
Is it safe to use AI tools in the workplace?
Yes, but businesses should create clear AI usage guidelines. Employees should avoid sharing sensitive information such as passwords, financial data, personal details, contracts, or confidential business information when using AI tools.
What are the benefits of integrating AI into business operations?
AI can increase efficiency, automate repetitive work, provide data-driven insights, support faster decision-making, and free up employees to focus on higher-value strategic work.
How can a business get started with AI?
Start by identifying repetitive or time-consuming tasks that could be automated. Experiment with AI tools for content creation, data analysis, or workflow support, and establish an internal AI policy to guide responsible use.
Related Links
- Everything You Need to Know About Search GPT
- Generative Engine Optimization: What You Need to Know
- How to Write Winning AI Chatbot Prompts
- Warning! Google Gemini AI Chatbot Has Security Risks
- 5 Free AI Tools for Marketing
- The GEO Formula: AI-Powered SEO Strategies
- AI in Digital Marketing
- Local SEO
- Organic Search (SEO)
- AI – Latest Insights, Applications, and Tools We Use
- The Secrets of AI Image Generation
- SEO Services Indianapolis
- Proof Point Podcast
- Let’s Talk


















